Category: You Asked, We Answered
What is a Developer Account on the App Stores?
Disambiguating ‘Developer Accounts’ and the Role of a Software Agency or Developer
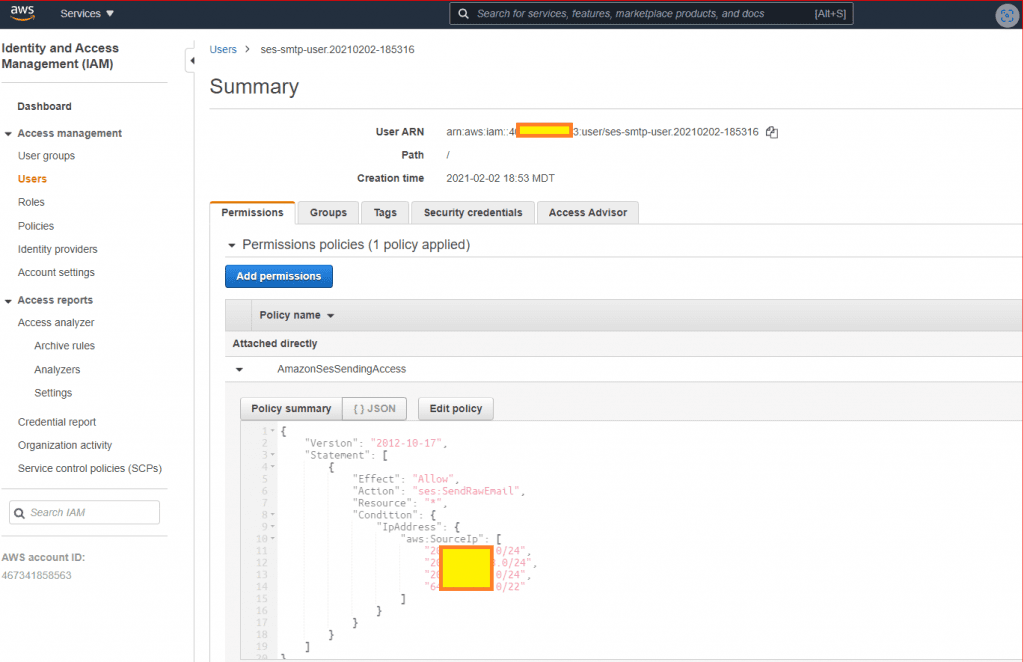
What is a ‘Developer Account’?
A developer account is the account required to publish apps on Google Play or Apple’s App Store. This account is owned by the person or business responsible for the app—usually the app’s owner—not by the person or agency that does the coding or technical work.
Do I need to be a developer to create a ‘Developer Account’?
No. You don’t need to know how to code to create a developer account. This account is for managing your app’s presence on the app stores, including publication, updates, and payment settings. The technical development can be handled by a software company or individual developers you hire.
Who should own the developer account?
The app owner (you or your business) should always own the developer account. Even if you hire a software company or a developer to build and manage your app, the account should stay under your control to manage ownership, payments, and app settings.
What’s the difference between a ‘developer account’ and a developer?
A ‘developer account’ is for managing the app’s store presence. A ‘developer’ refers to the person or team responsible for writing the code and building the app. You might hire a software company or agency to develop the app, but they do not own the account unless specifically transferred.
Can I give my developer access to my ‘developer account’?
Yes, both Google Play and Apple allow you to give a developer or software agency access without transferring ownership. You can assign specific roles with permissions tailored to the work they need to do, such as uploading app updates or managing listings.
What kind of access should I give my developer or software agency?
You should give your software agency or developer access to technical tasks such as uploading new app versions and managing the store listing. However, you should retain control over financial, legal, and account settings since they directly affect your ownership of the app.
What happens if I transfer my whole developer account to the developer or software company?
This is not recommended. If you transfer your account to the developer or software company, they gain control over the app’s ownership, payments, and store settings. To avoid complications, always maintain ownership of your developer account. Never share your credentials or password – instead use the tools in the App Store to invite your developers to work with your app.
How do I add a developer or software company to my Google Play Developer Account?
In the Google Play Console, you can add users from your hired software company or developers and assign them specific roles. This allows them to manage updates or other technical aspects without giving them access to sensitive areas like payments or legal settings.
How do I add a developer or software agency to my Apple Developer Account?
Through App Store Connect, you can invite your hired developers or software company and assign them roles such as ‘App Manager’ or ‘Developer.’ This allows them to manage app-related tasks while keeping account ownership in your hands.
Do Software Companies have their own Developer Account?
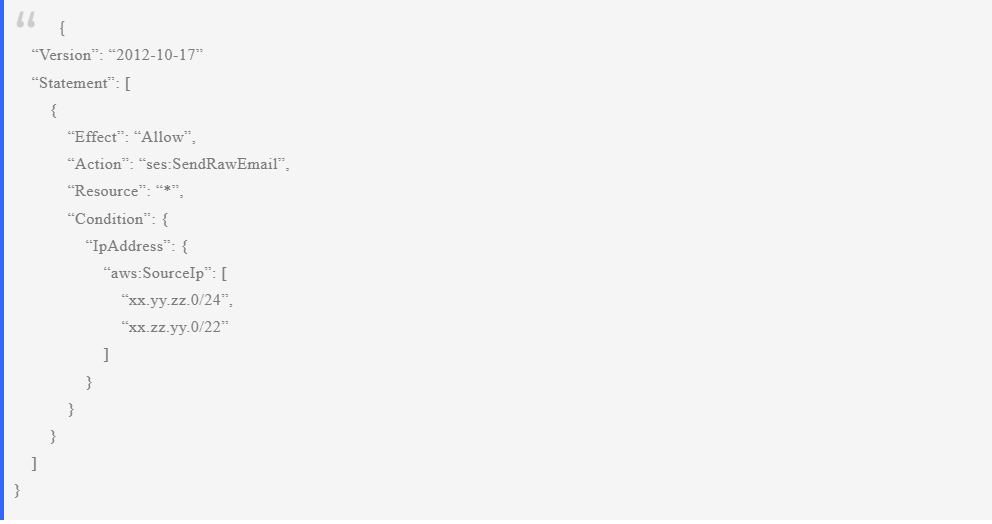
Yes, typically a software agency or the developer(or freelancer) will need their developer account to manage certain parts of your app’s store listing, particularly if they are handling multiple clients or apps. This account used by the software agency or the technical developer account is separate from the Developer Account, which remains under the control and ownership of the App’s owner
Do I need to take action even if I’ve hired a software agency?
Yes. Even with a software company or developers helping with the technical work, you will still need to manage certain aspects of your account. This can include legal updates, financial settings, and sometimes even specific actions related to the app’s publication that the hired company cannot perform on your behalf. Where possible the Software Agency is able to direct you to make changes in your account.
How do I, as an app owner, validate my developer account?
As the app owner, when the App Store asks you to validate your developer account – they are asking for you to confirm that your company is a real entity. (they are not asking for information on who your technical team is that is doing work on your application). Your Developer Account with the App Store represents your ownership and management of the app on the platform. To validate your account, ensure:
- The account is registered in your or your company’s name.
- The payment and legal details match your business information.
Remember, even though your software agency can assist with publishing and managing the listing, ownership and account details in your Developer Account (like agreeing to new terms or legal agreements) must be performed by you.
What is a user story?
User stories are a valuable tool for capturing software requirements in an easily understandable format. They help communicate the needs and expectations of users, allowing software developers to deliver targeted solutions. Here’s a description of how to format a user story and what should be included:
Format: A user story typically follows a simple template known as the “As a, I want, so that” format:
“As a {type of user}, I want {a feature or functionality} so that {a reason or benefit}.”
Components:
- Role/Persona: The user story begins by identifying the type of user or persona for whom the feature is intended. It provides context about the specific user or group of users who will benefit from the feature.
- Feature/Functionality: This part describes the desired feature or functionality in clear and concise terms. It should focus on what the user wants to accomplish or the problem they need to solve.
- Reason/Benefit: The reason or benefit section explains why the user wants the feature or functionality. It provides insight into the underlying motivation or desired outcome.
Example: As an online shopper, I want to view my order history so that I can track my previous purchases and quickly reorder items.
In this example, the user story identifies the persona (online shopper), the desired feature (view order history), and the reason/benefit (tracking previous purchases and reordering items).
Tips for Writing Effective User Stories:
- Keep it concise: User stories should be brief and focused. Avoid including technical details or implementation specifics. They should capture the “what” and “why,” leaving the “how” to the development team.
- Use a common language: User stories should be understandable to both technical and non-technical stakeholders. Avoid using jargon or technical terms that might confuse or exclude others.
- Collaborate and iterate: User stories are not set in stone. They should be a collaborative effort between stakeholders, product owners, and developers. Refine and iterate on user stories as you gain a deeper understanding of the user’s needs.
Using user stories can help transition to a more structured and effective way of describing software requirements.
When Should I Update My App?
How Can I Ensure I Possess My App’s Code?
What Is an App Prototype?
What Are 5 Things to Look for in an App Development Company?
Where Is Mobile App Data Stored?

Are your apps stored on a sim card? A microSD card? Internal storage? On the cloud? We answer this question below.
Note: This is an expanded/enhanced article of “Are Apps Stored on my SIM card?” If you prefer to read the original article, click here.
To make a long story short, the data that makes an app: video, audio, and music files, documents, downloaded content, and user accounts can be stored in a number of locations. It depends on the app itself, the amount of storage the app requires, how often the app updates, and the settings on your mobile device to where the app and subsequent files are stored. In this article, we will clarify where app data for a mobile device is stored.
This article goes through the following and describes whether app data is stored there and how:
MicroSD Cards
A MicroSD Card is a type of removable flash memory card that is used for storing data, pictures, music, and video. They are used in many devices including smartphones, tablets, digital cameras, and video cameras.
MicroSD Cards are tiny, usually about 15mmx11mm X 1mm, which is about the size of a thumbnail. When used, they are placed directly inside the device, usually in a slot labeled “microSD”. The microSD card can then be easily removed and replaced if needed.
A microSD card stores data in the form of binary code, and a single microSD card can vary greatly in storage capacity, from 2GB to over 1TB. As technology continues to improve, this storage capacity is likely to increase as well.
MicroSD cards can store app data including game data, downloaded content, and user accounts. Most devices with microSD cards are able to automatically detect and save app info to the microSD card, but, in some cases depending on the device, you have to enable this feature. Additionally, some apps require that you manually select the microSD card as the location to save app info.
It’s worth noting that not all smart phones are equipped with ports for microSD cards, Some of the newer models of iPhones as well as some flagship Android models no longer have microSD ports. Instead, they have larger internal storage and rely on cloud storage to back up data should it become necessary.

A MicroSD Card
SIM Cards
A SIM card (Subscriber Identity Module) is about the same size as a microSD card and is also placed inside of a mobile device, usually by the smartphone dealer when the phone is taken in to be activated. Due to these similarities, many are under the misconception that the SIM card can also save app information and, should the card be removed, they would lose that information.
A sim card does not store app data or any type of personal information. It does store the user’s phone number, network authorization data, and text messages. It allows users to switch their service provider by transferring their information to a new SIM card. It also allows users to transmit data and send voice calls and receive calls from other people through their phone.
Another common misconception about SIM cards is that a cell phone will not work if a SIM card is not in place. This is not true. Without a SIM card, you will not be able to place calls or send messages, but a phone can still pick up a wi-fi signal and most of its other features will still function.

A SIM Card
Internal storage
If you are downloading an app on your phone, the most likely place for the app info to go is to the phone’s internal memory. Generally, when you download an app, it will be stored in a specific folder on the device itself.
This folder is usually referred to as the “Applications” folder. Once the app is installed, you can access it by opening that folder and tapping on the icon of the app. From there, you can change many of the app’s settings as well as disable it or uninstall it.
As of this writing, the standard amount of internal storage for an iPhone or Android is 128GB with up to 1TB available. With that amount of storage now available on mobile devices and even more expected in the near future, some devices have chosen to forego the microSD card slot.
If a phone now risks running low on internal storage, such items as pictures and videos can be transferred to cloud storage. Cloud storage is considered by many to be much more reliable than microSD cards or older methods of portable memory.
Cloud Storage
Cloud storage is a component of cloud computing and is the practice of storing data in a remote, online location instead of a physical storage device. Cloud storage works by transferring data from a user’s computer or smart device to a remote server, usually via the internet. This keeps data safe from many computer breaches since the data is not stored on a device.
The data is then stored in a server which is owned and maintained by a cloud storage provider. The data is securely backed up on the server and users can access it from any device with an internet connection. Google offers Google Drive, which is is one option for free cloud storage and cloud backup.
SaaS business software is typically stored on the cloud. This gives users great computing ability without taking up any internal storage on their computer or devices. Such SaaS software frequently offers exceptional collaboration tools for teams to use. In addition, users can access the software and their information from anywhere, making it extremely convenient. Some business software such as Google Drive and Microsoft Office 365 allow you to store files on the cloud and also download them to your device when needed.
Generally, apps that require more storage space such as large file sharing or audio/video streaming apps will be stored more on the cloud than other types of apps. Additionally, apps that require frequent updates such as messaging, social media, and gaming apps will also be stored on the cloud to ensure that users are able to access the latest version of the app without as many crashes or downtimes.
Apps that require more computing power and require complex calculations also tend to be stored on the cloud to ensure that users have access to the highest level of computing power available.
Apps that are stored on the cloud tend to be much more scalable. Being on the cloud allows an app to handle large amounts of data and traffic and tackle sudden spikes in user demand.
Matraex is a premier app and software development company located in southwest Idaho. Our mission is to answer business and consumer questions regarding app and software development so they can make the best decisions for their circumstances.
We hope that you will look through our content for answers. We would also love the chance to answer your questions directly. Feel free to contact us, call us at (208) 344-1115, or leave a question on our Google Business Profile. We look forward to hearing from you.
Sign up to receive answers to your questions delivered directly to your inbox!